The landscape of customer experience has undergone a dramatic transformation over the past decade. What began as simple rule-based chatbots offering basic responses to predefined queries has evolved into sophisticated autonomous AI agents capable of understanding context, learning from interactions, and providing personalized solutions in real-time. This evolution represents not just a technological advancement but a fundamental shift in how businesses engage with their customers.
The AI agent market, estimated at $5.4 billion in 2024, is projected to grow to a staggering $47.1 billion by 2030, driven by increasing demand for self-service customer experiences and the need for businesses to provide 24/7 support without scaling human resources proportionally. As cloud computing makes AI agent deployment more accessible, businesses of all sizes can now leverage these technologies to transform their customer experience strategies.
This article explores the evolution of AI agents in customer experience, from their humble beginnings to the current state of the art, and provides insights into how businesses can effectively test, implement, and optimize these systems to gain a competitive edge.
The Evolution of Customer Experience Automation
First Generation: Rule-Based Chatbots
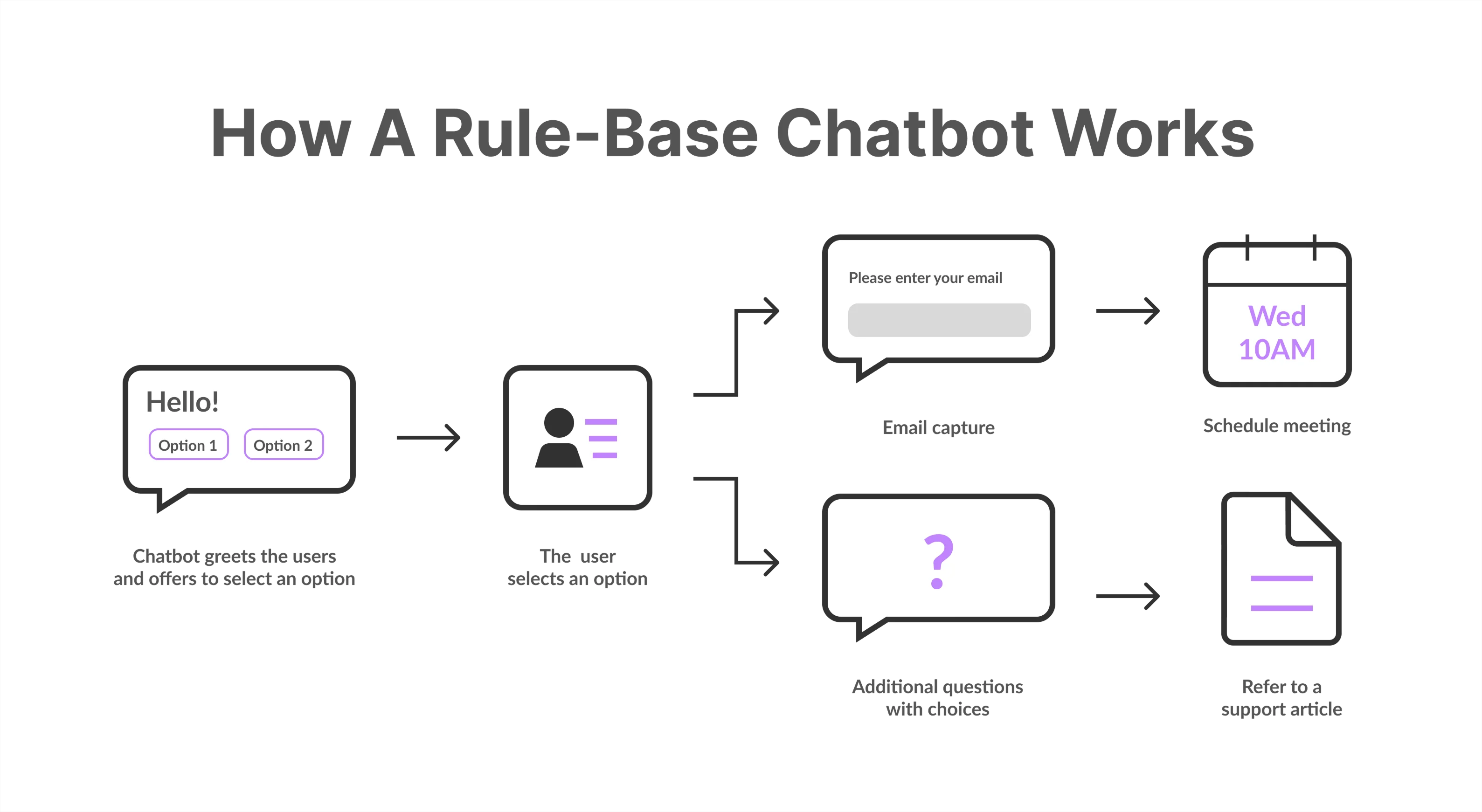
The first generation of automated customer service tools emerged in the early 2000s in the form of rule-based chatbots. These systems operated on simple if-then logic, where specific customer inputs would trigger predefined responses.
Key characteristics of rule-based chatbots:
- Decision tree structures: Conversations followed predetermined paths based on user selections
- Keyword matching: Systems identified specific words to determine appropriate responses
- Limited flexibility: Could only respond to anticipated questions within their programming
- No learning capabilities: Unable to improve from interactions without manual updates
- Scripted interactions: Responses were entirely pre-written by developers
While revolutionary at the time, these systems were notoriously frustrating for users who needed help with anything outside their narrowly defined parameters. A slight variation in phrasing could break the entire interaction, leading to the dreaded “I don’t understand” response or being trapped in an endless loop of irrelevant suggestions.
Despite these limitations, rule-based chatbots provided a foundation for automating simple, repetitive queries, allowing human agents to focus on more complex issues. They demonstrated the potential for automation in customer experience while highlighting the need for more sophisticated solutions.
Second Generation: NLP-Enhanced Virtual Assistants
By the mid-2010s, advances in Natural Language Processing (NLP) enabled the development of more flexible virtual assistants. These systems could understand variations in language, recognize intents behind queries, and provide more natural-sounding responses.
Key advancements in NLP-enhanced virtual assistants:
- Intent recognition: Could identify the purpose of a query despite variations in phrasing
- Entity extraction: Able to identify specific pieces of information within a request
- Sentiment analysis: Basic ability to detect customer frustration or satisfaction
- Limited contextual understanding: Could maintain some continuity across a conversation
- Improved error handling: Better fallback mechanisms when queries fell outside capabilities
These systems represented a significant improvement over their rule-based predecessors. Customers could phrase their questions more naturally, and the systems could handle a wider range of inquiries without breaking down. Companies like Apple, Google, Amazon, and Microsoft invested heavily in this technology, leading to the creation of Siri, Google Assistant, Alexa, and Cortana.
However, these second-generation systems still relied heavily on predefined responses and lacked true understanding of complex queries. They struggled with ambiguity, multi-part questions, and maintaining context over extended interactions.
Third Generation: AI-Powered Conversational Agents
Around 2018-2020, machine learning and deep learning techniques enabled the development of more sophisticated AI-powered conversational agents. These systems incorporated statistical models that allowed them to learn from data and improve over time.
Key capabilities of AI-powered conversational agents:
- Machine learning foundations: Improved through exposure to more conversation data
- Better contextual awareness: Could maintain conversation history more effectively
- Personalization capabilities: Able to tailor responses based on user profiles and history
- Integration with knowledge bases: Could pull information from structured databases
- Multi-turn conversations: Managed more complex, multi-step interactions
These systems represented a significant leap forward, with the ability to handle more complex queries and provide more personalized experiences. They could be integrated with CRM systems and other business tools, allowing them to access customer data and provide more relevant assistance.
Companies implemented these solutions to handle a wider range of customer service tasks, from account management to product recommendations. These agents could understand not just what customers were asking for but also why they were asking, enabling more helpful and relevant responses.
Fourth Generation: LLM-Powered Autonomous AI Agents
With the introduction of Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini, we entered the current generation of customer experience automation: autonomous AI agents . These systems leverage the immense knowledge and reasoning capabilities of foundation models combined with specialized components for task execution.
Defining characteristics of autonomous AI agents:
- Foundation model intelligence: Built on LLMs with billions of parameters
- Reasoning capabilities: Can think through complex problems step-by-step
- Tool integration: Can access and use external tools and APIs to complete tasks
- Multi-modal understanding: Process text, images, and sometimes audio inputs
- Memory systems: Maintain short-term and long-term information about interactions
- Self-improvement: Learn from successful and unsuccessful interactions
- Near-human interaction quality: Communicate in a natural, conversational manner
These autonomous agents represent a paradigm shift in customer experience automation. Rather than simply responding to queries, they can proactively solve problems, make recommendations, and handle complex workflows without human intervention.
For example, an autonomous AI agent in e-commerce might:
- Understand a customer’s query about product recommendations
- Access the inventory database to check current stock
- Review the customer’s purchase history for preferences
- Consider current promotions and seasonality
- Generate personalized recommendations with explanations
- Process a purchase if requested
- Schedule delivery and follow up with tracking information
All of this can happen in a single, seamless conversation that feels natural to the customer.
The Anatomy of Modern AI Agents for Customer Experience
Modern AI agents for customer experience are sophisticated systems composed of multiple components working together. Understanding this architecture is essential for businesses looking to implement, test, and optimize these systems.
Core Components
Foundation Model Layer
At the heart of modern AI agents is the foundation model, typically a Large Language Model (LLM) like GPT-4, Claude, or Gemini. This component provides:
- Natural language understanding: Comprehends customer inputs regardless of phrasing
- Natural language generation: Creates human-like responses that feel conversational
- Reasoning capabilities: Works through complex requests logically
- General knowledge: Brings broad understanding of products, services, and common issues
The foundation model serves as the “brain” of the AI agent, processing inputs and generating outputs based on its training and fine-tuning.
Knowledge Integration Layer
Modern AI agents connect to various knowledge sources to provide accurate, up-to-date information:
- Knowledge bases: Structured repositories of product information, FAQs, and procedures
- Document retrieval systems: Access to product manuals, policy documents, and guides
- Customer data: Integration with CRM systems for personalized assistance
- Vector databases: Semantic search capabilities for finding relevant information quickly
This layer typically implements Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to enhance the foundation model’s responses with specific, accurate information from trusted sources.
Tool Use and Integration Layer
To take actions on behalf of customers, AI agents need to interface with various business systems:
- API connections: Links to order management, billing, shipping, and other systems
- Authentication systems: Secure access to customer accounts
- Payment processing: Ability to handle transactions when authorized
- Ticketing systems: Creation and management of support tickets
- Calendar systems: Scheduling appointments or follow-ups
This capability to use tools transforms AI agents from mere conversational interfaces into autonomous systems that can complete tasks end-to-end.
Memory Systems
Effective customer interactions require maintaining context over time:
- Short-term memory: Tracking the current conversation flow
- Session memory: Remembering what’s been discussed in the current interaction
- Long-term memory: Recalling previous interactions with the same customer
- Organizational memory: Learning from interactions across all customers
These memory systems enable personalized experiences and continuous improvement of the agent’s capabilities.
Monitoring and Safety Layer
To ensure quality interactions and protect both customers and the business:
- Content filtering: Preventing harmful or inappropriate responses
- Confidence scoring: Assessing the reliability of generated responses
- Fallback mechanisms: Graceful handling of situations beyond the agent’s capabilities
- Human handoff protocols: Seamless transition to human agents when needed
This layer is crucial for maintaining trust and ensuring that autonomous agents operate within appropriate boundaries.
Testing AI Agents for Customer Experience
Successfully implementing AI agents requires rigorous testing across multiple dimensions. Unlike traditional software, AI systems introduce unique challenges that demand specialized testing approaches.
Functional Testing
Basic functional testing ensures the agent can perform its core tasks:
- Conversation flow testing: Verifying that the agent can maintain coherent conversations
- Task completion testing: Confirming that the agent can fulfill common customer requests
- Integration testing: Ensuring proper connectivity with business systems
- Scenario-based testing: Running through common customer journeys end-to-end
Performance Testing
AI agents must perform efficiently at scale:
- Response time testing: Measuring how quickly the agent responds to queries
- Concurrency testing: Assessing performance under multiple simultaneous interactions
- Load testing: Determining capacity limits under heavy usage
- Stress testing: Identifying breaking points and recovery capabilities
Accuracy Testing
The quality of information provided is paramount:
- Factual accuracy: Verifying that information provided is correct
- Consistency testing: Ensuring similar questions receive compatible answers
- Knowledge boundary testing: Identifying what the agent does and doesn’t know
- Update validation: Confirming that new information is correctly incorporated
Usability Testing
The customer experience must be smooth and intuitive:
- Conversation quality assessment: Evaluating naturalness and clarity of interactions
- User satisfaction metrics: Measuring customer ratings of interactions
- Accessibility testing: Ensuring the agent is usable by people with disabilities
- Multi-modal testing: Verifying functionality across text, voice, and visual interfaces
Security and Compliance Testing
AI agents must protect data and meet regulatory requirements:
- Data handling validation: Ensuring proper protection of sensitive information
- Authentication testing: Verifying secure identity verification processes
- Prompt injection testing: Attempting to manipulate the agent through malicious inputs
- Compliance verification: Confirming adherence to relevant regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.)
Specialized AI Testing
Unique to AI systems are tests that evaluate their behavior beyond simple functionality:
- Hallucination testing: Identifying when agents generate false information
- Bias evaluation: Detecting and addressing unfair or prejudiced responses
- Edge case handling: Assessing responses to unusual or unexpected queries
- Adversarial testing: Deliberately attempting to provoke inappropriate responses
Continuous Testing
As AI agents learn and evolve, ongoing testing becomes essential:
- Regression testing: Ensuring new capabilities don’t break existing functionality
- A/B testing: Comparing different agent versions to identify improvements
- Comparative testing: Benchmarking against human agents or competitor systems
- Long-term performance monitoring: Tracking metrics over time to identify drift
Case Studies: Real-World Success Stories
To illustrate the impact of AI agents, let’s examine several case studies showcasing concrete data and business outcomes.
Public Service Credit Union: Reducing Agent Workload
Industry: Banking and Financial Services
Challenge: Agents were overwhelmed with repetitive queries such as balance checks and routing number requests, leading to low productivity and burnout.
Solution: Using Kore.ai’s BankAssist conversational AI solution, the credit union automated 70% of inbound service calls with an intelligent virtual assistant.
Results:
- 24% reduction in agent-serviced calls within 30 days.
- 70% containment rate (queries resolved without human intervention).
- Increased agent productivity, enabling staff to focus on revenue-generating calls.
Bosch: Streamlining Global Operations
Industry: Engineering and Technology
Challenge: Bosch aimed to enhance employee experiences by automating HR functions and IT support across 400,000+ employees.
Solution: Leveraging Cognigy.AI, Bosch deployed robust self-service solutions that integrate seamlessly with their existing workflows.
Results:
- Reduced average employee query resolution time by 60%.
- Enhanced employee satisfaction and streamlined IT support processes.
Orange: 24/7 Multi-Channel Support
Industry: Telecommunications
Challenge: With over 273 million customers globally, Orange needed to reduce phone and eChat volume while improving first-line technical troubleshooting.
Solution: The company developed Djingo, a contextual AI assistant powered by Rasa , enabling customers to resolve internet and TV issues on platforms like Facebook Messenger.
Results:
- Automated responses to the most common issues, reducing agent workload.
- Improved customer satisfaction by offering 24/7 support and faster resolutions.
Henkel: Enhancing Brand Loyalty
Industry: FMCG
Challenge: Henkel wanted to offer instant stain treatment advice to customers to enhance loyalty and trust in its Laundry & Home Care division.
Solution: Using Cognigy.AI’s conversational platform, Henkel deployed an assistant capable of identifying 2,500+ substance variations and providing accurate cleaning advice.
Results:
- Increased brand loyalty and customer engagement.
- Enhanced consumer trust in Henkel’s mission of “cleaner living.”
The Business Impact of Autonomous AI Agents
The evolution of AI agents from rule-based chatbots to intelligent autonomous systems marks a pivotal moment in customer experience automation. The implementation of autonomous AI agents for customer experience delivers significant business value across multiple dimensions.
Quantitative Benefits
Operational Efficiency
- Cost reduction: AI agents typically cost 60-80% less per interaction than human agents
- Increased capacity: Handle up to 10x more simultaneous interactions
- Faster resolution: Average resolution time decreases by 40-60%
- 24/7 availability: Eliminate wait times during off-hours and peak periods
Revenue Enhancement
- Conversion rate improvements: Personalized recommendations increase conversions by 15-30%
- Larger average order values: Contextual upselling increases AOV by 10-25%
- Reduced cart abandonment: Immediate assistance decreases abandonment by 15-20%
- Expanded selling hours: Generate revenue during times when human agents are unavailable
Qualitative Improvements
Customer Experience
- Consistency: Every customer receives the same high-quality service
- Personalization at scale: Tailored interactions based on individual preferences and history
- Reduced friction: Seamless handling of routine tasks without transfers or delays
- Channel flexibility: Consistent experience across web, mobile, voice, and messaging
Competitive Advantage
- Innovation perception: Position your brand as technologically advanced
- Data-driven insights: Gain deeper understanding of customer needs and pain points
- Agility: Rapidly adapt to changing customer preferences and market conditions
- Resource reallocation: Shift human talent to high-value, complex interactions
Future Trends in AI Agents for Customer Experience
As technology continues to evolve, several emerging trends will shape the future of AI agents in customer experience:
Multi-Modal Interactions
Future AI agents will seamlessly integrate multiple communication modes:
- Visual understanding: Processing and responding to images and videos
- Voice-first interactions: Natural spoken conversations with human-like qualities
- Gesture recognition: Interpreting physical movements in augmented reality settings
- Emotional intelligence: Recognizing and responding to customer emotions
These capabilities will create more natural, intuitive interactions that mirror human communication patterns.
Proactive and Predictive Engagement
Rather than waiting for customer inquiries, advanced AI agents will:
- Anticipate needs: Predict what customers might need based on behavior patterns
- Prevent problems: Identify and address potential issues before they affect customers
- Suggest improvements: Recommend product or service enhancements based on usage
- Time-sensitive outreach: Contact customers at optimal moments for engagement
This shift from reactive to proactive support will fundamentally change customer expectations.
Ecosystem Orchestration
AI agents will increasingly coordinate across complex business ecosystems:
- Cross-department coordination: Orchestrating actions across multiple business units
- Partner network integration: Seamless handoffs to third-party service providers
- Multi-agent collaboration: Specialized agents working together on complex tasks
- End-to-end journey management: Guiding customers through complete processes
These capabilities will enable handling of sophisticated customer journeys that span multiple systems and entities.
Hyper-Personalization
Future AI agents will deliver unprecedented levels of personalization:
- Dynamic personality adaptation: Adjusting communication style to match customer preferences
- Life context awareness: Understanding broader customer circumstances beyond transactions, such as the customer’s journey
- Preference learning: Continuously refining understanding of individual tastes
- Anticipatory personalization: Preemptively adapting based on predicted preferences or behavioral changes
This deep personalization will create experiences that feel genuinely tailored to each individual.
Ethical and Responsible AI
As AI agents become more integrated into customer experiences, ethical considerations will gain prominence:
- Transparency mechanisms: Clearly indicating when customers are interacting with AI
- Explainable decisions: Providing rationales for recommendations and actions
- Bias mitigation: Actively identifying and addressing unfair treatment
- Privacy controls: Giving customers agency over their data and interaction history
These practices will build trust in AI agents and ensure they serve all customers equitably.
Conclusion
The evolution of AI agents in customer experience—from simple rule-based chatbots to sophisticated autonomous systems—represents one of the most significant transformations in how businesses interact with their customers. Today’s AI agents, powered by large language models and integrated with robust tools and knowledge bases, can deliver personalized, efficient service at scale while continuously improving through learning.
For businesses looking to implement AI technologies, thorough testing is essential before launch. Platforms like Genezio offer advanced testing services for AI agents, allowing you to simulate hundreds of conversations with your target audience and analyze the generated responses. This approach ensures performance optimization, content relevance, and successful implementation. Get your free AI performance report today and book a demo to see how your chatbot performs with real users.
As we look to the future, the continued advancement of AI technologies promises even more transformative possibilities for customer experience. Businesses that embrace these technologies now will be well-positioned to meet evolving customer expectations and gain a significant competitive advantage in their markets.
The journey from simple chatbots to autonomous AI agents isn’t just a technological evolution—it’s a fundamental rethinking of the customer experience paradigm. For businesses ready to make this transition, the rewards in efficiency, customer satisfaction, and business growth are substantial and within reach.
Article contents
Subscribe to our newsletter
Genezio is a serverless platform for building full-stack web and mobile applications in a scalable and cost-efficient way.
Related articles
More from AI
Quality Monitoring Software: How To Make Sure AI Agents Benefit Support and Customers
Luis Minvielle
May 23, 2025







