Horatiu Voicu
Mar 04, 2025
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, artificial intelligence and intelligent agents have moved from science fiction to practical business tools. Whether you’re a developer looking to integrate AI capabilities into your applications or a business owner seeking to leverage automation for competitive advantage, understanding AI agents is becoming increasingly critical.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the fundamentals of intelligent agents in artificial intelligence, their various types, how they function, and practical examples of their implementation. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how AI agency can transform your projects and business operations.
What Are AI Agents?
An intelligent agent is a software entity that perceives its environment, makes decisions, and takes actions to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional software programs that merely follow predefined instructions, AI agents can adapt their behavior based on environmental feedback and learning from experiences.
These agents operate on the core principle of autonomy—they can function without direct human intervention while still adhering to the objectives set by their human creators. This combination of independence and goal-oriented behavior makes artificial intelligence agents particularly valuable for handling complex, dynamic tasks.
Key Characteristics of Intelligent Agents
What separates an intelligent agent in artificial intelligence from conventional software? Several distinct characteristics:
- Autonomy: Operates without direct human intervention
- Reactivity: Responds to changes in its environment
- Proactivity: Takes initiative toward achieving goals
- Social ability: Interacts with other agents or humans
- Learning capability: Improves performance over time through experience
- Goal-oriented: Works to achieve specific objectives
- Memory: Maintains and updates relevant information
An advanced AI agent will demonstrate all these qualities to varying degrees, depending on its design and purpose.
The Agent Loop: How AI Agents Work
At the heart of every intelligent agent in AI is what’s known as the agent loop or cognitive cycle:
- Observe: The agent gathers information from its environment
- Orient: It processes and interprets this information
- Decide: Based on this interpretation, it selects an appropriate action
- Act: It executes the chosen action
- Learn: It updates its knowledge based on outcomes
This cycle, sometimes referred to as OODA (Observe, Orient, Decide, Act), forms the fundamental operational pattern for artificial intelligence and intelligent agents. The sophistication of each step determines the agent’s overall capabilities.

Types of AI Agents
The world of intelligent agents in AI encompasses several distinct categories, each with specific capabilities and applications:
Simple Reflex Agents
These basic agents respond directly to current environmental inputs based on condition-action rules. They don’t maintain any internal state or consider the history of their interactions.
Example: A thermostat that turns heating on when the temperature drops below a threshold.
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Unlike simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents can maintain an internal representation of the environment, making them more adaptable to changing conditions. These agents maintain an internal model of the world, allowing them to handle partially observable environments by tracking internal state.
Example: A robotic vacuum cleaner that navigates a room by detecting obstacles and remembering their locations to avoid collisions. It updates its internal model of the environment as it moves but does not plan an optimal cleaning path in advance.
Goal-Based Agents
These more sophisticated agents evaluate different actions based on how they contribute to achieving defined goals.
Example: A self-driving car that encounters an accident on the road will autonomously adjust its direction to avoid the obstacle. By predicting the outcomes of its movements, the vehicle can plan an efficient and safe path forward.
Utility-Based Agents
These agents make decisions based on a utility function that quantifies the desirability of different states, enabling them to choose the most beneficial action rather than just any goal-achieving step.
Example: An AI system that optimizes digital advertising campaigns by intelligently allocating budgets across platforms based on real-time ROI metrics..
Learning Agents
The most advanced category, these agents can improve their performance over time through experience.
Example: A recommendation system, like those used by Netflix or Amazon Prime, that learns from user preferences to suggest better content over time.
How AI Agents Function: The PEAS Framework
To understand how an intelligent agent in artificial intelligence operates, we use the PEAS framework:
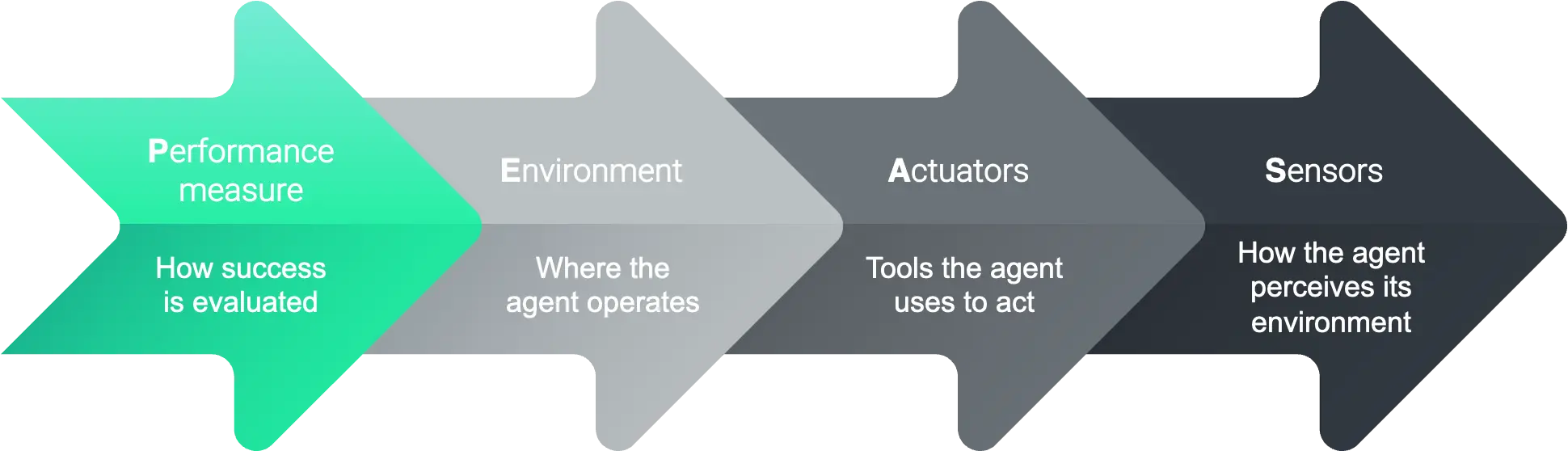
To see how this works in practice, let’s apply the PEAS framework to an e-commerce recommendation agent:
| Component | E-commerce Recommendation Agent |
|---|---|
| Performance measure | Conversion rate, average order value |
| Environment | Website, user behavior data, product catalog |
| Actuators | Product recommendations, promotional offers |
| Sensors | User clicks, purchase history, browse patterns |
Understanding this operational structure clarifies how different AI intelligent agents function in their specific domains.
The Anatomy of Modern AI Agents
Modern AI agents integrate several key components that enable sophisticated behavior and adaptability.
Foundation Models
Many modern agents are built on large language models (LLMs) or other foundation models that provide:
- Robust natural language understanding and generation
- Reasoning capabilities across diverse domains
- Knowledge derived from extensive training data
Tool Use and Integration
Advanced AI agents have the capability to access and utilize external tools and APIs, allowing them to extend their functionality beyond predefined tasks. They can retrieve information from databases or the web, ensuring access to up-to-date and relevant data. Additionally, these agents can execute code to perform computations or automate tasks, enhancing efficiency and adaptability. They are also able to interface with other software systems, enabling seamless integration and interaction across different platforms.
Memory Systems
Sophisticated AI agents utilize multi-layered memory systems to enhance their performance and adaptability. They rely on short-term context to manage immediate conversations, ensuring coherent and relevant interactions. Long-term storage allows them to retain persistent information for future reference. Episodic memory enables them to recall specific past interactions, while conceptual memory helps store abstract knowledge, improving their ability to understand and generate meaningful responses.
Planning and Reasoning Modules
The most advanced AI agents incorporate sophisticated reasoning and planning capabilities to enhance problem-solving and decision-making. They employ task decomposition to break complex goals into manageable steps, ensuring efficient execution. Recursive reasoning allows them to tackle multi-stage problems by systematically analyzing each layer. These agents can generate and test hypotheses, refining their approach based on outcomes. Additionally, they engage in self-reflection to evaluate performance and adjust strategies, leading to continuous improvement and adaptability.
Real-World Applications of AI Agents
Intelligent agents have proliferated across industries, transforming operations in numerous fields through their ability to automate complex tasks and enhance human capabilities.
Business Process Automation
AI agents are revolutionizing back-office operations by streamlining document management, workflow orchestration, and financial processes. These systems extract and categorize information from unstructured documents, manage approval processes with intelligent exception handling, and detect discrepancies in financial transactions—all while reducing manual intervention and improving accuracy.
Customer Experience Enhancement
The artificial intelligence agency approach is fundamentally changing customer interactions through multifaceted engagement strategies. Conversational AI now provides around-the-clock support across various communication channels, while personalization engines tailor content and recommendations to individual preferences. These systems are further enhanced by sentiment analysis capabilities that can detect customer emotions and escalate issues when human intervention becomes necessary.
Research and Knowledge Work
AI agents are accelerating knowledge-intensive tasks by serving as research assistants that find, summarize, and synthesize information from vast data sources. They analyze complex datasets to identify meaningful patterns and anomalies, while also drafting initial versions of reports, articles, and presentations to increase knowledge worker productivity.
Software Development
The software development lifecycle has been enhanced by AI assistance by providing context-aware code completion and suggestions. These systems also identify potential bugs and security vulnerabilities during development, while automatically generating clear documentation explaining code functionality and system architecture.
Healthcare Innovation
In the medical field, intelligent agents are making significant contributions by analyzing medical images to identify potential issues that might be missed by human evaluation alone. They suggest personalized treatment plans based on patient data and medical literature, while continuously monitoring patient vitals to alert care teams about changes that require immediate attention.
Case Study: Intelligent Agent in E-commerce
Let’s examine how an online retailer implemented an artificial intelligence and intelligent agents approach to transform their business:
Challenge: The company was struggling with shopping cart abandonment rates of 75%, significantly above industry average.
Solution: They deployed a multi-agent system including:
- A behavioral analysis agent that identified patterns leading to abandonment
- A timing agent that determined optimal moments for intervention
- A personalization agent that crafted tailored incentives based on user history
- An interaction agent that delivered these incentives through appropriate channels
Results:
- Cart abandonment decreased by 31%
- Conversion rate increased by 22%
- Average order value improved by 17%
This case demonstrates how an intelligent agent can address complex business challenges through coordinated specialization.
Building Your First AI Agent: A Developer’s Primer
For developers interested in creating an AI agent, here’s a simplified roadmap:
1. Define Your Agent’s Purpose
Start by clearly articulating:
- The specific problems your agent will solve
- The environment in which it will operate
- The performance metrics that define success
2. Select Your Technology Stack
Common frameworks for developing intelligent agents include:
- TensorFlow Agents and Stable Baselines for reinforcement learning, providing pre-built implementations of RL algorithms.
- Rasa and Dialogflow for building conversational AI agents with natural language understanding and dialogue management.
- LangChain and LlamaIndex for developing LLM-based agents , enabling efficient orchestration of large language models and knowledge retrieval.
- Ray RLlib for scalable and distributed reinforcement learning, optimizing training for complex environments.
3. Design Your Agent Architecture
When designing your AI agent, define its structural components to ensure optimal performance:
- Perception modules – Process and interpret input data from various sources.
- Reasoning approach – Choose between rule-based (deterministic), learning-based (adaptive), or a hybrid model.
- Action capabilities – Define how the agent interacts with users, systems, or its environment.
- Memory systems – Implement short-term, long-term, episodic, or conceptual memory for information storage and retrieval.
- Learning mechanisms (if applicable) – Enable continuous adaptation and improvement based on new data and experiences.
4. Implement Iteratively
Start with a minimal viable agent and expand gradually:
- Begin with simple rule-based behavior – Establish a basic functional model.
- Add complexity gradually – Introduce learning capabilities, memory, and reasoning enhancements over time.
- Test extensively in controlled environments – Identify and resolve issues before wider deployment.
- Gather feedback and refine – Continuously improve based on real-world usage and insights.
5. Deploy and Monitor
When launching your AI agent, ensure stability and long-term success:
- Implement appropriate safeguards – Address security, ethical concerns, and potential biases.
- Monitor performance metrics – Track accuracy, efficiency, and response times.
- Collect user feedback – Understand user interactions and refine accordingly.
- Establish continuous improvement cycles – Regularly update and optimize the agent based on new data and evolving needs.
The Agentic Stack: Deployment Infrastructure
When deploying AI agents, infrastructure becomes a critical consideration. An effective deployment stack typically includes:
Compute Resources
Agents require appropriate processing power:
- CPU/GPU/TPU resources for model inference
- Scaling capabilities to handle varying loads
- Memory allocation for context and reasoning
Communication Layers
Modern intelligent agent in artificial intelligence systems need:
- API gateways for external communication
- Message queues for asynchronous operations
- Webhooks for event-driven architecture
Monitoring and Logging
Effective operation demands:
- Performance telemetry
- Error tracking and alerting
- Usage analytics
- Audit trails for agent actions
Security Protocols
Responsible deployment requires:
- Authentication and authorization systems
- Data encryption
- Rate limiting
- Vulnerability management
Get Your AI Agent Development Checklist!
To streamline your AI agent development process, we’ve created a detailed, structured checklist that helps you prioritize tasks, track progress, and optimize implementation. Whether you’re a developer or a business owner, this Google Sheets template will guide you step by step.
Access the checklist and make a copy here: AI Agent Development Checklist
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite their potential, AI agents come with important challenges:
Technical Challenges
- Environmental complexity: Agents must navigate increasingly complex scenarios
- Generalization: Moving beyond specific domains remains difficult
- Explainability: Advanced agents often function as “black boxes”
- Resource requirements: Sophisticated agents need substantial computational resources
Ethical Considerations
Every artificial intelligence and intelligent agents implementation requires careful attention to:
- Transparency: Users should understand when they’re interacting with agents
- Bias mitigation: Agents can amplify existing biases in training data
- Privacy: Agent data collection practices must respect user privacy
- Accountability: Clear responsibility frameworks for agent actions are essential
- Alignment: Ensuring agent goals remain aligned with human values and intentions
The Future of AI Agents
As we look ahead, several trends are shaping the evolution of intelligent agents:
Multi-Agent Systems
Complex problems increasingly require collaboration between specialized agents, each handling different aspects of a task while coordinating their efforts.
Agent Personalization
Future AI agents will adapt not just to general patterns but to individual user preferences, communication styles, and specific needs.
Augmented Intelligence
Rather than replacing human capabilities, many agents will focus on enhancing human decision-making by reducing cognitive load and providing contextual information.
Agentic Workflows
We’ll see increasing adoption of agent-orchestrated workflows, where multiple intelligent agents work together in coordinated sequences to accomplish complex tasks that span different domains and expertise areas.
Conclusion
The field of AI agents represents one of the most dynamic and promising areas of technological development today. From simple task automation to complex decision support, intelligent agents are transforming how businesses operate and how developers approach problem-solving.
Whether you’re looking to implement existing agent technologies or develop custom solutions, understanding the fundamentals outlined in this guide provides an essential foundation for success in the evolving landscape of artificial intelligence agency.
As you consider your next steps, remember that the most successful agent implementations start with clearly defined problems and thoughtfully designed architectures—technical sophistication alone doesn’t guarantee value.
Make your AI Agent trustworthy
Ready to safeguard your enterprise AI-powered chatbot against sophisticated threats? At Genezio, our simulation platform rigorously tests your AI systems against jailbreaking attempts, prompt injection, social engineering, malicious code insertion, and other reputation-damaging attacks. Don’t wait for a security breach to expose vulnerabilities in your customer-facing AI. Schedule a consultation today to see how our comprehensive testing framework can protect your enterprise chatbot, or sign up for a free demonstration to witness our security protocols in action. Secure your AI , protect your reputation, and build customer trust with Genezio.
This article is part of our ongoing series on artificial intelligence implementation strategies. Check back for future installments covering advanced agent design patterns, integration approaches, and industry-specific applications.
Article contents
Subscribe to our newsletter
DeployApps is a serverless platform for building full-stack web and mobile applications in a scalable and cost-efficient way.
Related articles
More from AI
Quality Monitoring Software: How To Make Sure AI Agents Benefit Support and Customers
Luis Minvielle
May 23, 2025







