Cristi Miloiu
Dec 10, 2024
Hi! I’m Cristi Miloiu, and in this article, I’ll walk you through building a ChatGPT-powered chat app using Flask, Python, and the OpenAI API. We’ll also cover deploying your app seamlessly with Genezio, a powerful cloud deployment platform.
If you’re short on time and prefer a ready-to-go solution, click here to deploy the app instantly to your account!
Have questions or suggestions? Feel free to contact me at cristi@genezio.com.
Here’s what we’ll achieve by the end of this tutorial:
- A functional Flask-based ChatGPT app with a responsive user interface.
- Seamless deployment using Genezio for scalability and production readiness.
Step-by-Step Guide
Before you begin, make sure you have Python and pip installed on your machine.
Step 1: Install Flask and Required Libraries
First, let’s set up a virtual environment and install the necessary dependencies:
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # On Windows: venv\Scripts\activate
pip3 install flask openai python-dotenv
pip3 freeze > requirements.txt
Explanation:
venvcreates an isolated Python environment for the project.- Flask is the web framework.
openaiallows communication with the OpenAI API.python-dotenvhelps manage environment variables.requirements.txtensures consistent dependencies when deploying the app.
Step 2: Create the index.py file
Next, create the main file of the application, index.py, with the following content:
from flask import Flask, request, Response, render_template
import openai
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# Initialize application
app = Flask(__name__)
messages = []
# OpenAI Configuration
load_dotenv()
openai.api_key = os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY')
def get_openai_response(message):
"""Separate function to handle OpenAI communication"""
if not openai.api_key:
raise ValueError("API key is not set!")
try:
client = openai.OpenAI(api_key=openai.api_key)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": message}],
stream=False
)
if not response or not response.choices:
raise ValueError("No response received from API")
return response.choices[0].message.content
except openai.AuthenticationError:
raise ValueError("Invalid API key")
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError(f"Error communicating with OpenAI: {str(e)}")
@app.route('/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def chat():
if request.method == 'POST':
message = request.form.get('message', '')
if not openai.api_key:
return render_template('index.html',
messages=messages,
error="OpenAI API key is not set!")
if message:
try:
answer = get_openai_response(message)
messages.extend([
{"is_user": True, "q": message},
{"is_user": False, "a": answer}
])
except Exception as e:
app.logger.error(f"Error in chat route: {str(e)}")
return render_template('index.html',
messages=messages,
error=f"An error occurred while processing your request: {str(e)}")
return render_template('index.html', messages=messages)
@app.route('/reset', methods=['POST'])
def reset():
global messages
messages = []
return render_template('index.html', messages=messages)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
Explanation: The app has two routes:
/ ->handles displaying and updating the chat./reset ->clears the chat history.
The function get_openai_response sends user input to the OpenAI API and retrieves a response.
Step 3: Create a templates Folder and index.html File
Create a folder named templates and add a file index.html:
mkdir templates
touch templates/index.html
This folder will store the HTML template used to display the chat interface.
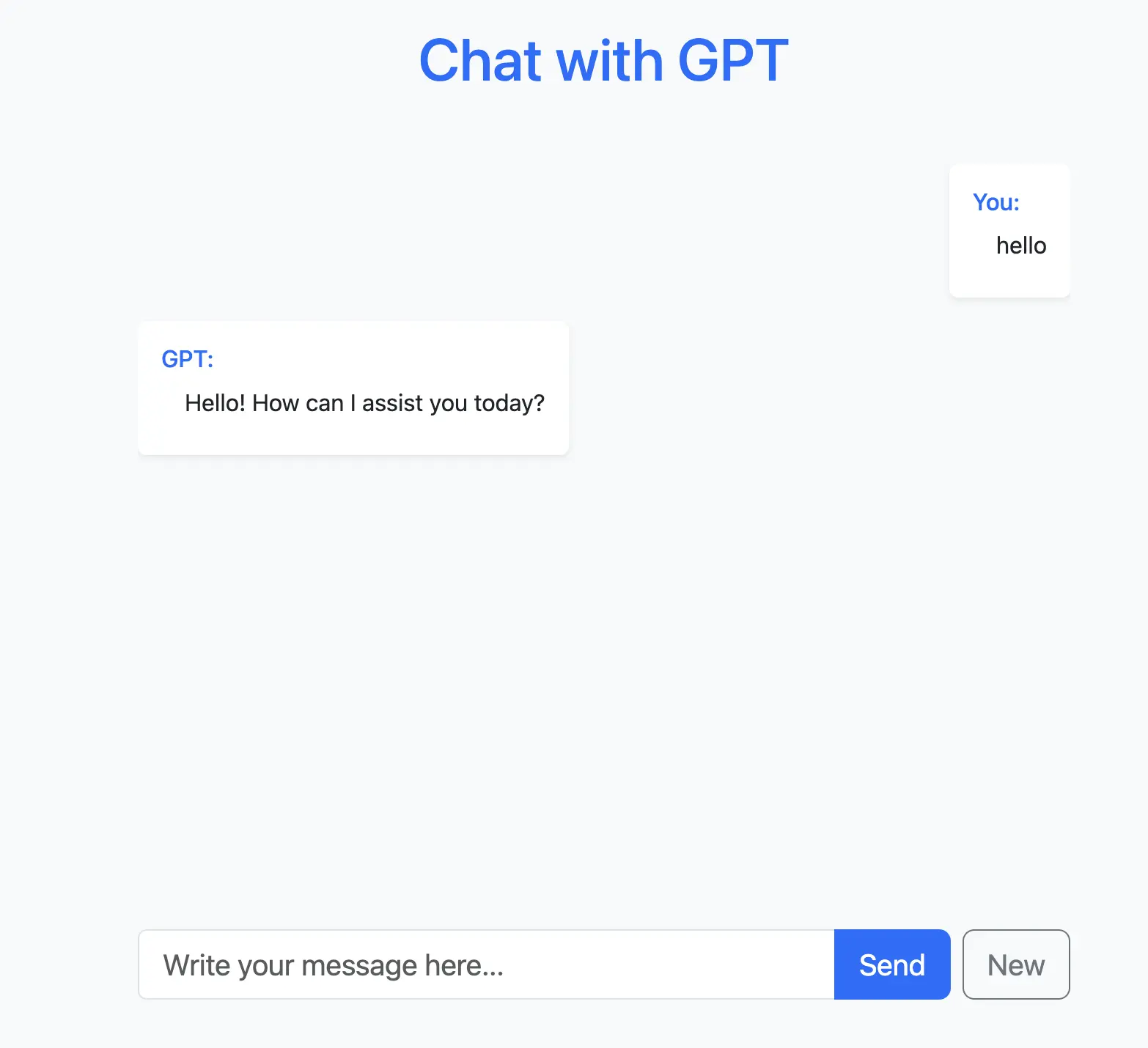
Step 4: Complete the index.html File
Here’s the content of the index.html file:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Chat with GPT</title>
<link
href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.3/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"
rel="stylesheet"
/>
</head>
<body class="bg-light min-vh-100 d-flex flex-column">
<div class="container py-5 flex-grow-1 d-flex flex-column">
<div class="row justify-content-center flex-grow-1">
<div class="col-12 col-md-8 col-lg-6 d-flex flex-column">
<h1 class="text-center mb-5 text-primary">Chat with GPT</h1>
{% if error %}
<div class="alert alert-danger mb-4" role="alert">{{ error }}</div>
{% endif %}
<div class="flex-grow-1 overflow-auto mb-4" style="max-height: 60vh;">
{% for message in messages %}
<div
class="d-flex {{ 'justify-content-end' if message.is_user else 'justify-content-start' }} mb-3"
>
<div class="card shadow-sm border-0" style="max-width: 75%;">
<div class="card-body">
<div class="mb-2">
<h3 class="h6 text-primary">{{ 'You' if message.is_user else 'GPT' }}:</h3>
<p class="mb-0 ps-3">{{ message.q if message.is_user else message.a }}</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{% endfor %}
</div>
<div class="d-flex gap-2">
<form method="POST" action="/" class="flex-grow-1">
<div class="input-group">
<input
type="text"
name="message"
class="form-control form-control-lg rounded-start"
placeholder="Write your message here..."
required
/>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary btn-lg">Send</button>
</div>
</form>
<form method="POST" action="/reset">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-outline-secondary btn-lg">New</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.3/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
- Displays the chat messages with user and GPT labels.
- Includes input fields and buttons for sending messages or resetting the chat.
Step 5: Add a .env File
Create a .env file to securely store your OpenAI API key:
OPENAI_API_KEY=<your_openai_key>
This file ensures that sensitive data like API keys aren’t hardcoded in the application.
Step 6: Install genezio CLI
Run the following command:
npm install -g genezio
Step 7: Test Locally
Run your app locally using Genezio:
genezio local
This command runs your app in a local development environment.
Step 8: Create the configuration file
Run the following command:
genezio analyze
Explanation:
- Genezio scans your project to create a configuration file,
genezio.yaml. - During this process, you’ll be prompted to enter the project name and region in the terminal.
Step 9: Deploy your app with Genezio
Finally, deploy your app to the cloud with a single command:
genezio deploy
Your app will be live at a custom subdomain, such as
https://your-app-name.app.genez.io.
You can continue to manage, test, update and monitor your project from the genezio dashboard.
Why use Genezio for deployment?
- Simplified Deployment: One-command deployment makes getting your app live easy.
- Scalability: Automatically scale your app as user demand grows.
- Built-in Monitoring: Manage and monitor your app from the Genezio dashboard.
With this guide, you’ve learned to:
- Build a Flask-based ChatGPT app using the OpenAI API.
Deploy and manage your app seamlessly with Genezio.
If you have questions or feedback, feel free to reach out to me at cristi@genezio.com.
The codebase for this tutorial is open-source, and you can find it in this Github repository .
Article contents
Subscribe to our newsletter
Genezio is a serverless platform for building full-stack web and mobile applications in a scalable and cost-efficient way.
Related articles
More from Tutorials